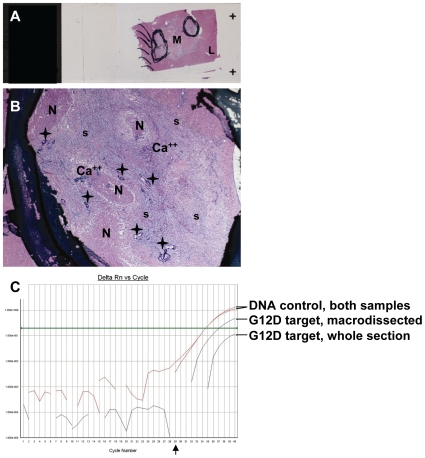
Figure 5. Typical example of a diagnostic case with very low content in neoplastic cells.
If macrodissection is avoided in such cases, erroneous results are likely to be obtained. A, whole section of the CRC metastatic site (M) surrounded by normal liver (L). Circled areas are marked for macrodissection. In B, the metastatic site is largely composed of necrotic (N) and calcified (Ca++) elements within a loose stroma (s), while neoplastic cells (asterisks) correspond to <<1% in the whole section (A) and to ∼10% in the macrodissected areas (B). Two DNA samples were extracted from this specimen, one upon macrodissection and one from the whole section. As shown in C, although both DNA samples were of the same unfavorable quality (DNA control Ct∼34.5), it was possible to identify the G12D mutation in the macrodissected sample, while the sample obtained from the whole section appeared as wild type. Arrow in C, Ct = 29.