Figure 1.
The Silent K+ Channel KC1 Interacts with the SNARE SYP121 in Arabidopsis.
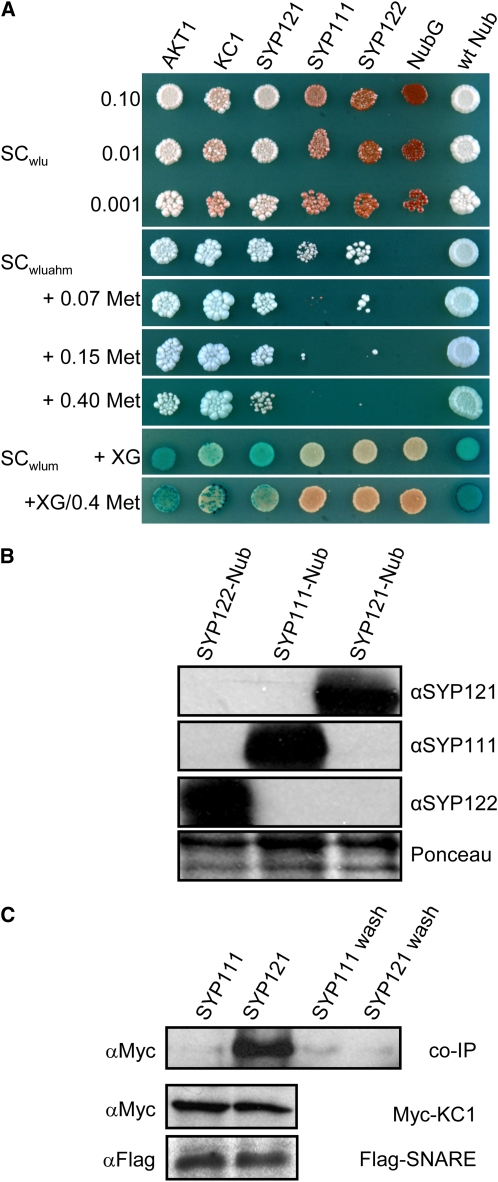
(A) Yeast mating-based split-ubiquitin assay for interaction with KC1-Cub. Yeast diploids created with Nub-X constructs of AKT1, KC1, SYP121, SYP111, SYP122, and controls (negative, NubG; positive, wild-type Nub) spotted (left to right) on synthetic complete (SC) medium without Trp, Leu, and Ura (SCwlu) to verify crossing and test for adenine synthesis (white colonies, top panel). SC without Trp, Leu, Ura, Ade, His, and Met (SCwluahm) used to verify Ade- and His-independent growth (second panel), and the addition of 0.07, 0.15, and 0.40 mM Met (next three panels) used to verify interaction at lower KC1-Cub expression levels. SC medium without Trp, Leu, Ura, and Met (SCwlum; last two panels) alone and with addition of 0.4 mM Met used with an overlay of X-Gal–containing agarose to assay β-galactosidase activity (Obrdlik et al., 2004). Serial dilutions 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001 of diploid cultures as indicated for spots on SCwlu. Otherwise, only 0.1 dilutions are shown. Note KC1 interaction with AKT1, itself, and SYP121 and the absence of specific interaction with SYP111 and SYP122.
(B) Verification of prey protein expression in diploid yeasts carrying KC1-Cub and Nub-SNAREs. Protein gel blot analysis of total protein extracted from yeast diploids expressing KC1-Cub with Nub-SYP122, Nub-SYP111, and Nub-SYP121 using antibodies specific for SYP122, SYP111, or SYP121 (top panels). Ponceau S stain was used as loading control (bottom panel).
(C) Coimmunoprecipitation of Myc-tagged KC1 by retention with Flag-tagged SYP121 on anti-Flag-coupled Sepharose. Protein gel blot analysis (top, left to right) of eluates coimmunoprecipitating with Flag-tagged SYP111, with SYP121, and the precipitated terminal washes prior to elution from each, respectively, probed with anti-Myc antibody. Control protein gel blots (bottom) show equivalent levels of expression for KC1 and for the SNAREs in each solubilized fraction after coexpression in Sf9 insect cells.