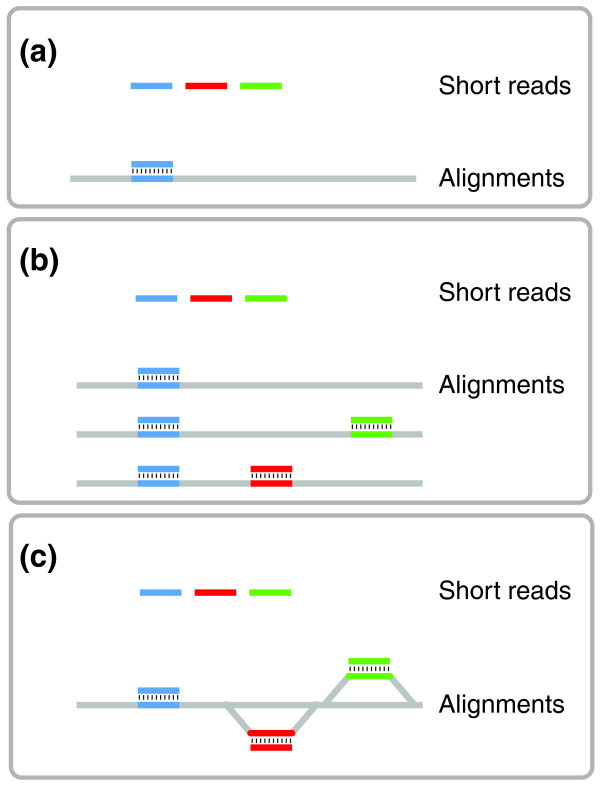
Figure 1.
Efficient alignments against multiple genomes. (a) Only reads that are sufficiently similar can be aligned against a single reference. (b) Separate alignment against multiple genomes allows access to divergent regions, but results in redundant alignments of reads that match all targets (blue). (c) Alignments against a graph index representing multiple genomes provide access to divergent regions without redundant alignments.