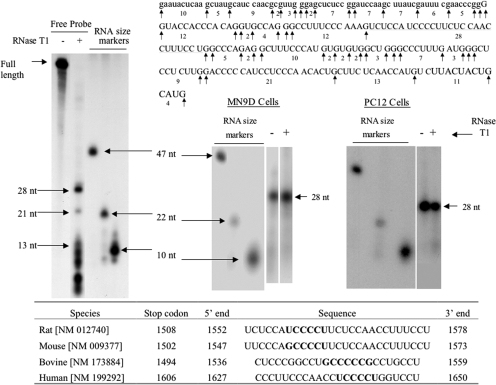
Fig. 3.
RNase T1 mapping depicts a 28-nt polypyrimidine binding site to which MN9D and PC12 cytoplasmic proteins bind to TH mRNA 3′-UTR. MN9D and PC12 cytoplasmic proteins were incubated with radiolabeled RNA probe encoding TH mRNA 3′-UTR sequences between the KpnI and SphI sites. The binding reaction was treated with RNase T1 and then subjected to electrophoresis on a nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel. The specifically bound RNA-protein complex was eluted from the gel and phenol-extracted to remove proteins. An aliquot of the eluate was subjected to electrophoresis on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel, whereas another aliquot was treated with RNase T1 before electrophoresis. The autoradiogram on the left side of the figure represents free radiolabeled RNA probe digested with RNase T1. Electrophoresis size markers are also designated on the autoradiogram. The TH mRNA (uppercase letters) and vector sequences (lowercase letters) comprising this probe along with the RNase T1 cutting sites are depicted in the figure. The two autoradiograms on the right side of the figure depict RNase T1 mapping experiments using MN9D and PC12 cytoplasmic proteins. The table at the bottom of the figure depicts polypyrimidine-rich sequences found in the 3′-UTRs of TH mRNAs from a number of species.