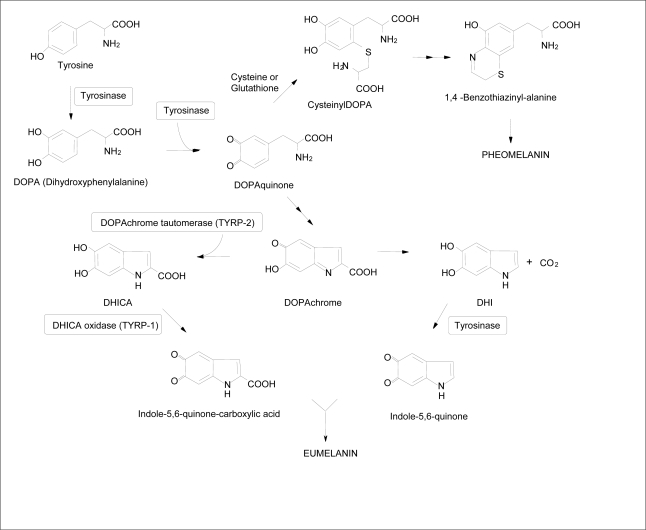
Scheme 1.
Process of melanogenesis within epidermal melanosomes.
Tyrosinase, the rate limiting enzyme of melanogenesis, catalyzes the hydroxylation of l-tyrosine to DOPA and the oxidation of DOPA to DOPAquinone. If cysteine or glutathione is present, it reacts with DOPAquinone to produce cysteinylDOPA and the benzothiazine derivatives of pheomelanin. As cysteine is diminished, DOPAquinone cyclizes into DOPAchrome. TYRP-2 catalyzes the tautomerization of DOPAchrome to 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA), which is later oxidized to DHICA-melanin subunits. The oxidation of DHICA to eumelanin is thought to be catalyzed by TYRP-1. In the absence of TYRP-2 the carboxylic acid moiety of DOPAchrome is spontaneously lost to form 5,6-dihydroxyindole (DHI). DHICA in conjunction with DHI comprise subunits of eumelanin [11,12].