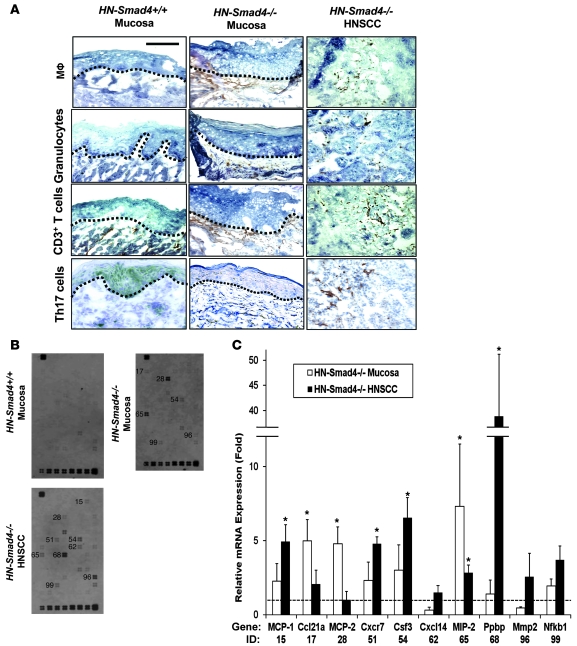
Figure 7. Increased inflammation and inflammatory chemokines in HN-Smad4–/– lesions.
(A) Immunostaining of HN-Smad4+/+ mucosa, HN-Smad4–/– mucosa, and HN-Smad4–/– HNSCCs with leukocyte markers. Macrophages (Mϕ) were stained with antibodies against F4/80; granulocytes with antibodies against Ly6G; T cells with antibodies against CD11b; and Th17 cells with antibodies against IL-17. The black dotted lines indicate the boundary between mucosa and stroma. HN-Smad4–/– mucosa has increased inflammatory markers in the underlying stroma compared with HN-Smad4+/+ mucosa, and HN-Smad4–/– HNSCCs have marked inflammation in the tumor stroma. 5–7 samples from each group were analyzed, and a representative image is presented. Scale bar: 40 μm (all panels). (B) Pathway-specific “Mouse Chemokines & Receptors” Superarray revealed increased inflammatory molecules in HN-Smad4–/– mucosa and HNSCC compared with HN-Smad4+/+ mucosa. Three samples per group of HN-Smad4+/+ mucosa, HN-Smad4–/– mucosa, and HN-Smad4–/– HNSCC were examined, and a representative blot from each group is presented. Genes with visible differences compared with HN-Smad4+/+ mucosa are labeled to the left with numbers that correspond to gene IDs quantified in C. (C) Relative mRNA expression (fold change) for each gene was calculated as optical density above adjacent background for HN-Smad4–/– mucosa and HN-Smad4–/– HNSCC samples compared with HN-Smad4+/+ samples. Gene names and IDs corresponding to numbers on the blot in B are displayed below. Error bars indicate SEM. *P < 0.05 versus HN-Smad4+/+ mucosa samples.