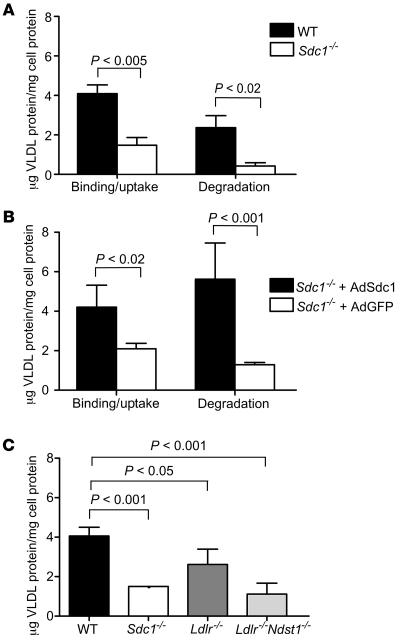
Figure 6. Binding, uptake, and degradation of VLDL at 37°C.
(A) Uptake and degradation of VLDL was measured in wild-type and mutant hepatocytes after 1 hour of incubation with 20 μg/ml of 125I-VLDL. The bars represent the sum of binding and internalization under these conditions, or the amount of degradation as determined by acid-soluble, non-chloroform–extractable counts in the medium. Binding plus uptake was reduced 2.7-fold in Sdc1–/– cells. Degradation was reduced by nearly 6-fold. (B) Hepatocytes isolated from Sdc1–/– mice treated with AdSdc1 showed enhanced binding and uptake and increased degradation of 125I-VLDL compared with hepatocytes isolated from Sdc1–/– mice treated with AdGFP (P < 0.02). (C) Binding and uptake were also measured in hepatocytes isolated from wild-type, Sdc1–/–, Ldlr–/–, and Ldlr–/–Ndst1f/fAlbCre+ mice. Uptake and binding were reduced 2-fold in the Sdc1–/– and Ldlr–/–Ndst1f/fAlbCre+ hepatocytes compared with wild-type (P < 0.001), while a slight change was observed in Ldlr–/– compared with wild-type (P < 0.05).