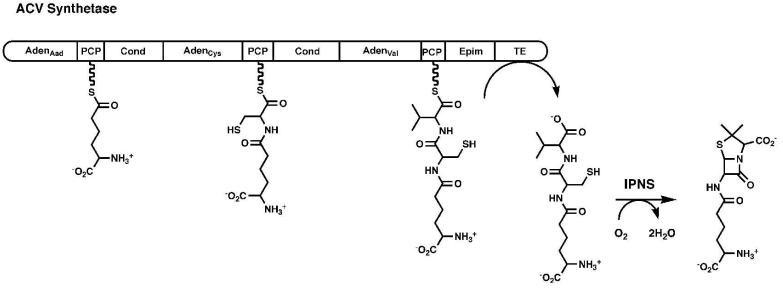
Figure 2. Modular Organization of the Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthetases.
A schematic representation is shown of the ACV synthetase, a three-module protein that is responsible for the synthesis of the linear tripeptide of α-aminoadipic acid (Aad), cysteine, and valine. The linear peptide is subsequently cyclized by the enzyme isopenicillin N synthase. Module 1 contains the adenylation domain and PCP for Aad. Module 2 contains the adenylation and PCP domain for cysteine, as well as the condensation domain that forms the peptide bond between Aad and Cys. The third module contains the adenylation and PCP domain for valine, an epimerization domain that converts l-Val to d-Val, and a condensation domain that transfers the upstream dipeptide to d-Val. The protein terminates with a thioesterase domain that releases the tripeptide.