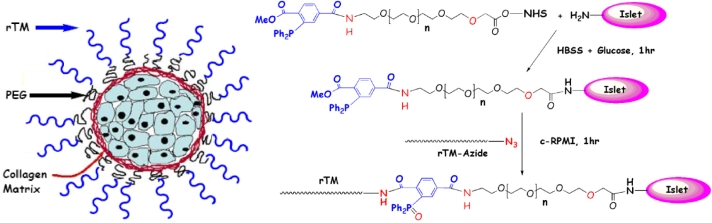
Figure 5.
Site-specific immobilization of thrombomodulin (TM) on pancreatic islets through use of Staudinger ligation. Using a biosynthetic approach, human TM was genetically engineered to contain a C-terminal azido (N3) group (rTM-azide), which can react chemoselectively with phosphine via Staudinger ligation. Phosphine groups were generated on the islet surface via active ester coupling between cell surface amines and a heterobifunctional phosphine-poly(ethylene glycol)- N-Hydroxysuccinimide linker, thereby allowing TM to be covalently tethered to islets in a chemo- and bio-orthogonal manner (Reprinted with permission from the American Chemical Society.152).