Figure 3a:
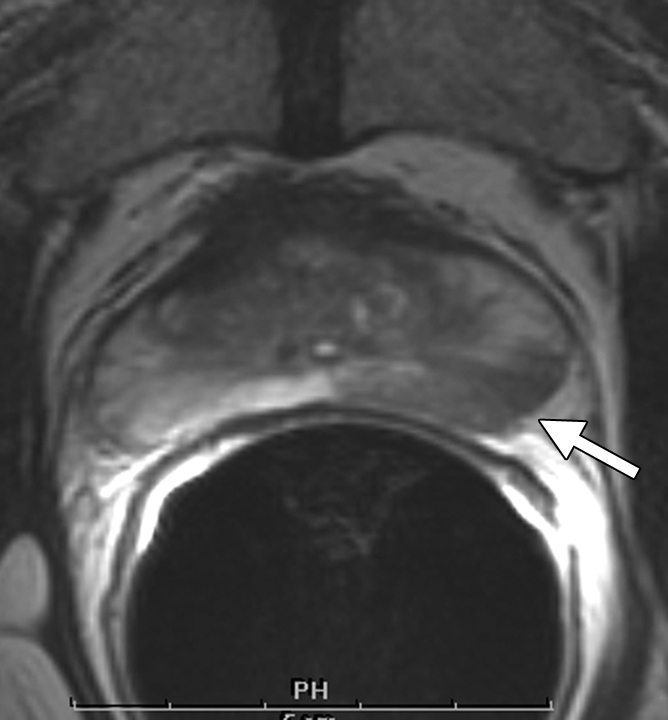
Clinical stage T1c prostate cancer in 52-year-old man. (a) Transverse T2-weighted endorectal MR image (4000/103, echo train length of 16, three acquired signals, 14-cm field of view, 256 × 192 matrix, 3-mm section thickness, no intersection gap) of prostate shows large area of abnormal signal intensity in left posterior peripheral zone. Mild capsular irregularity (arrow) is also present. These findings raise suspicion for prostate cancer with extracapsular extension. (b) MR spectroscopic grid overlaid on image in a. Asterisks indicate suspicious voxels in left posterior peripheral zone. MR spectroscopic imaging parameters are as follows: 1000/130, volume excitation with water and lipid suppression by means of spectral or spatial pulses, chemical shift imaging matrix of 16 × 8 × 8, 110 × 55 × 55-mm field of view, 6.9-mm spatial resolution, one acquired signal, and imaging time of 17 minutes. (c) Whole-mount step-section histopathologic specimen shows tumor (outlined in blue) with focal extracapsular extension (indicated by red dots) in left region. (Hematoxylin and eosin stain; original magnification, ×1.)
