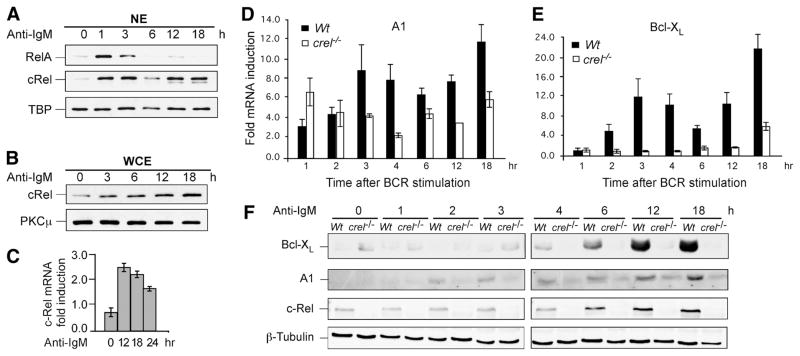
FIGURE 1.
BCR-Induced long-term induction of c-Rel coincides with expression of A1 and Bcl-xL. A and B, Splenic mature B cells were stimulated with anti-IgM F(ab′)2 (10 μg/ml) for indicated times; nuclear (NE) and whole cell extracts (WCE) were prepared as described in methods. Three micrograms NE or 10 μg WCE were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes, which were probed with Abs against NF-κB proteins RelA and c-Rel as indicated. TATA box binding protein and protein kinase C (PKC) μ were used as loading controls for NE and WCE, respectively. C, Analysis of BCR-induced c-Rel mRNA expression in naive splenic B cells. Cells were stimulated with 10 μg/ml anti-IgM F(ab′)2 for the indicated time points and RNA levels of c-Rel were determined by qRT-PCR. Relative fold induction of each gene was normalized to GAPDH and calibrated to the corresponding nonstimulated sample. Data are mean with SD from three experiments. D and E, c-Rel regulates long-term expression of A1 and Bcl-xL in mouse splenic B cells following BCR stimulation. Naive splenic B cells from WT and c-Rel deficient (c-rel−/−) splenic B cells were stimulated for the indicated times with 10 μg/ml anti-IgM F(ab′)2 and qRT-PCR was performed to determine the fold change in the steady-state levels of A1 and Bcl-xL mRNA compared with the endogenous control GAPDH and calibrated to the nonstimulated sample. Data are mean with SD from three experiments. F, Western blot analysis was performed on total cellular extracts from WT and c-Rel deficient (c-rel−/−) splenic B cells stimulated with anti-IgM F(ab′)2 for the indicated times. Blot was probed with anti-Bcl-xL, -A1, -c-Rel, and -β-Tubulin Abs. The data in all panels are representative of three independent experiments using different mice for each experiment.