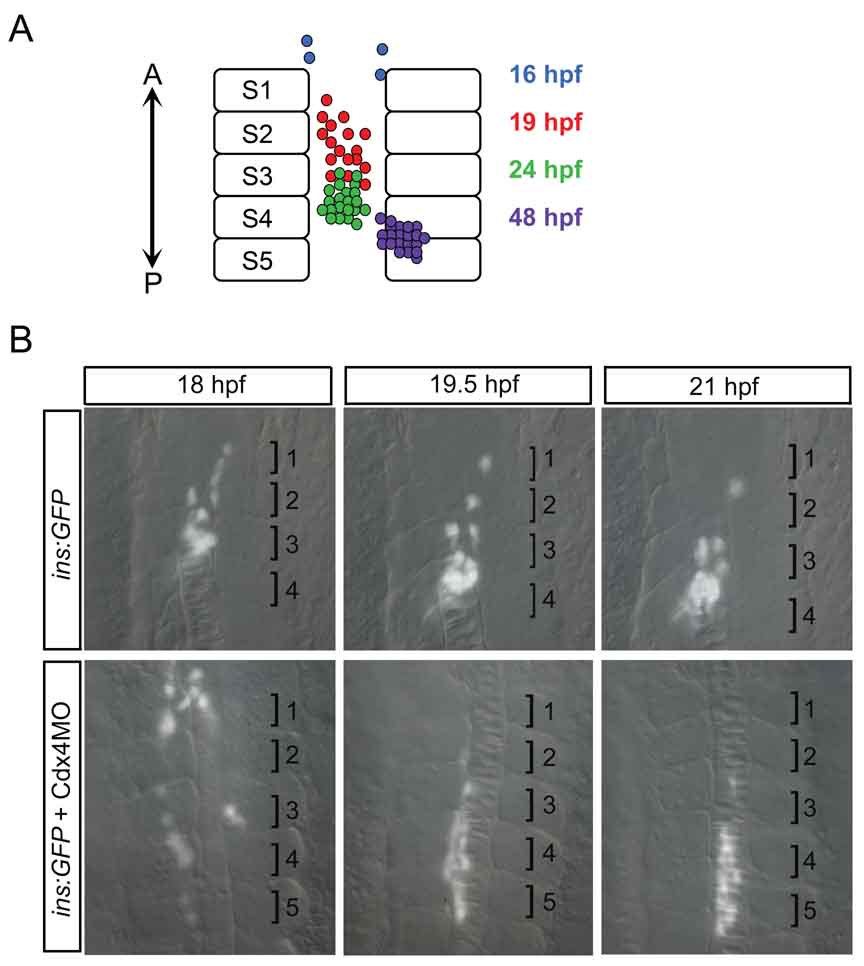
Figure 3. β-cell movement during islet formation.
A) Schematic of β-cell location during islet formation. Over time, insulin-positive β-cells increase in number, converge to form the islet, and move posteriorly. A, Anterior; P, Posterior; S, Somite. B) Live timelapse imaging reveals that β-cells move posteriorly during islet formation. Cdx4 knockdown results in farther movement of β-cells. Based on in situ hybridization, glucagon-positive β-cells and somatostatin2-positive β-cells are also initially located anteriorly in the trunk and subsequently surround the β-cell cluster within the more posteriorly located islet. It is thus likely that α- and δ-cells move posteriorly, similar to the β-cell movement revealed by live timelapse imaging. Brightfield and fluorescent images of insulin:GFP transgenics taken in dorsal view at 200x magnification and merged. Numbered brackets indicate somites.