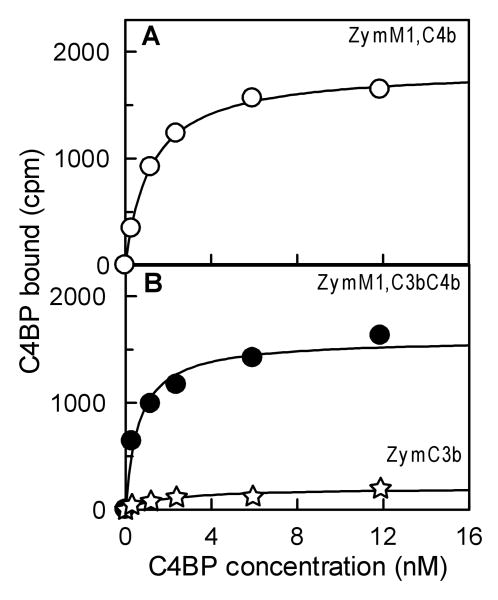
Fig. 3.
Equilibrium binding of C4BP to surface-bound C4b alone, C3b alone, and C4b-C3b complexes on zymosan. (A). C4BP binding to surface-bound C4b was measured as the amount of 125I-C4BP bound as cpm to ZymM1,C4b (○) under equilibrium conditions. ZymM1,C4b (0.44×106) bearing 59,000 C4b/Zym was incubated for 45 min at 37 °C with indicated concentration of 125I-C4BP (4.1×105 cpm/μg). The y axis represents the amount of radiolabeled C4BP bound to ZymM1C4b as cpm. The data were fit by nonlinear regression to a one-site binding equation to obtain the apparent binding constant (Kd). (B). C4BP binding to surface-bound C4b-C3b complexes was analyzed as described in Fig. 3(A) except that 0.44×106 ZymM1,C3bC4b bearing 54,000 C4b and 362,000 C3b/Zym was incubated with radiolabeled 125I-C4BP (4.1×105 cpm/μg). C4BP binding to zymosan bearing only C3b was also analyzed by incubating ZymC3b bearing 181,000 C3b/Zym with radiolabeled 125I-C4BP (7.65×105 cpm/μg). Data obtained with 0.84×106 ZymC3b was normalized for 0.44×106 ZymM1,C4b as well as for the specific activity of 125I-C4BP used and are shown in the figure. Symbols: ZymM1,C4bC3b (●); ZymC3b (✯).