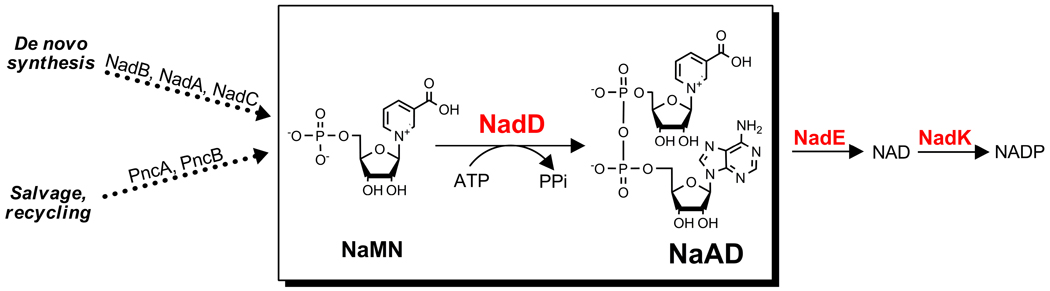
Figure 1. NAD(P)-biosynthesis pathways in bacteria.
NadD target enzyme is conserved in most bacteria. NaMN, a common biosynthetic intermediate in the salvage and de novo NAD biosynthetic pathways, is the substrate for NadD. The ATP substrate acts as the adenylyl moiety donor for NaMN, yielding PPi and NaAD. The latter product is then amidated (and phosphorylated) to give NAD and NADP.