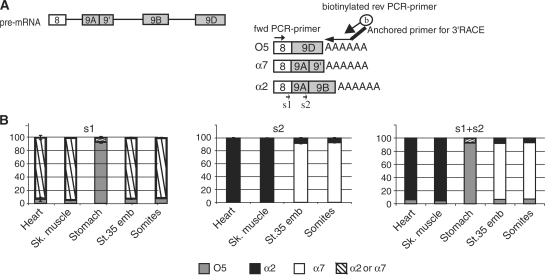
Figure 6.
Combined PASP and 3′RACE to analyse splicing of alternative 3′ terminal exons. (A) Schematic drawing of the 3′ terminal part of Xenopus α-tropomyosin pre-mRNA. Constitutive exon 8 can be spliced to exon 9D to generate isoform O5. Alternatively, it can be spliced to exon 9A9′. Exon 9A9′ can be used as the terminal exon (yielding isoform α7) or can be spliced to exon 9B via an alternative internal 5′ splice site to create isoform α2. In 3′RACE-PASP, an anchored oligo(dT) primer is used for RT, and a biotinylated reverse oligonucleotide corresponding to the anchor is used for PCR together with a forward primer in constitutive exon 8. Sequencing primer s1 hybridizes within constitutive exon 8, to discriminate between exon 9D, isoform O5, and 9A, isoforms α2 plus α7. Sequencing primer s2 hybridizes within exon 9A, to discriminate between exon 9′, isoform α7, and 9B, isoform α2. (B) 3′RACE-PASP of α-tropomyosin in the indicated tissues. Shown are the results obtained using sequencing primers 1 and 2 (mean ± SD of three different animals), and the results calculated from combining these two sequencings.