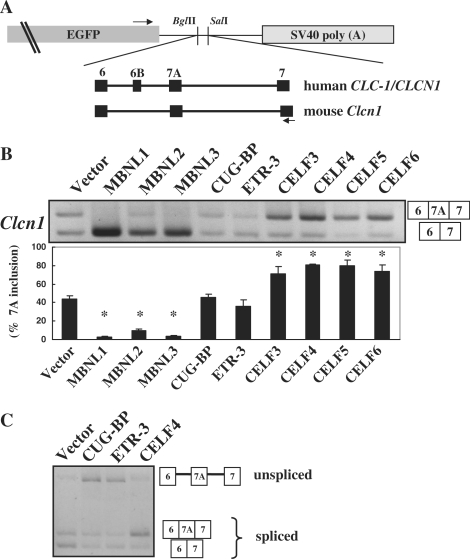
Figure 1.
Splicing regulation of MBNL and CELF proteins. (A) Structure of chloride channel minigenes. Both human CLCN1/ClC-1 and mouse Clcn1 minigenes were subcloned between the BglII and SalI sites of pEGFP-C1. Black boxes represent exons of the minigenes. Arrows indicate the position of primers used in the splicing assays. Exon 6B is a human-specific exon and is absent in Clcn1. (B) Splicing regulation of Clcn1 by MBNL and CELF proteins. Representative results of cellular splicing assays using the Clcn1 minigene in COS-7 cells. The upper bands correspond to a splice product containing exon 7A, whereas lower bands correspond to a splice product lacking exon 7A. Bar chart shows quantified results of exon 7A inclusion (mean ± SD, n = 3). Statistical significance was analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Dunnett's multiple comparisons. All MBNL proteins and CELF proteins except for CUG-BP and ETR-3 showed significant differences (*P < 0.0001) compared to the empty vector. (C) CUG-BP and ETR-3 increased an unspliced product of the Clcn1 minigene. Structures of PCR products are indicated.