Figure 6.
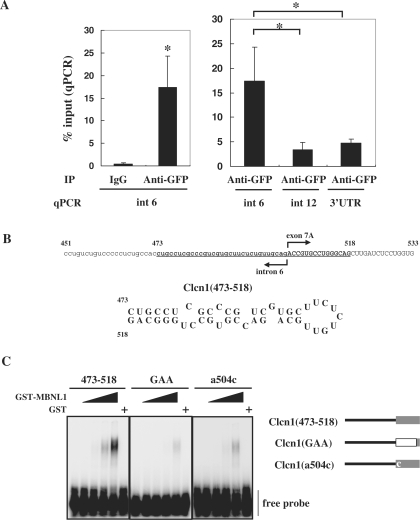
MBNL1 associates with Clcn1 RNA. (A) The intracellular association between EGFP-MBNL140 and the transcript of endogenous Clcn1 was analyzed by RIP. The cell lysate of a cell line stably expressing EGFP-MBNL1 was used for immunoprecipitation. The RNA fraction co-precipitated with anti-GFP antibody or IgG was reverse-transcribed. The amount of Clcn1 (pre-)mRNA was quantified by real-time quantitative PCR using a primer set for the indicated regions of the Clcn1 gene (n = 5). Bars represent the amount of Clcn1 RNA co-precipitated with anti-GFP antibody or control IgG normalized by the amount of the Clcn1 RNA in the input fraction (mean ± SD). Left: EGFP-MBNL1 was co-immunoprecipitated with RNA fragments containing Clcn1 intron 6 by GFP antibody but not control IgG (*P < 0.01, two-tailed t-test). Right: RIP analysis of multiple Clcn1 regions. Three regions of Clcn1 (intron 6, intron 12 and 3′-UTR) were amplified from immunoprecipitates of the GFP antibody. Intron 6 was significantly more enriched than the other regions (*P < 0.01, ANOVA and Tukey's test). (B) A hairpin structure predicted in the putative MBNL1-responsive region of Clcn1. Nucleotides 473–518 of Clcn1 are indicated in boldface (upper). Predicted secondary structure of the fragment Clcn1(473–518) (lower). (C) Binding between GST-MBNL1 and Clcn1(473–518) or its mutants was examined by gel shift analysis (left). 32P-labeled probes were incubated with or without GST-MBNL1 (0.225, 0.45, 0.9, 1.8 μM) or GST (1.8 μM). The reaction mixture was separated by native PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. Structure of probes used in gel shift analysis (right). In the Clcn1(GAA) mutant, the first 12 nt of exon 7A are substituted by (GAA)4 repeats. The Clcn1(a504c) mutant contains a point mutation of the first nucleotide of exon 7A but is otherwise the same as Clcn1(473–518).