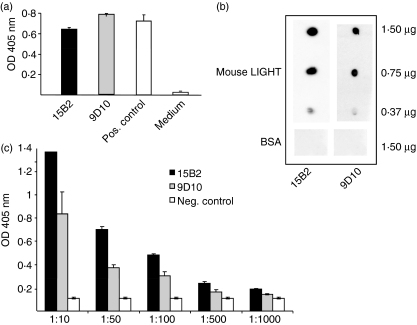
Figure 2.
Characterization of anti-mouse LIGHT (lymphotoxin-like inducible protein that competes with glycoprotein D for binding herpesvirus entry mediator on T cells) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). (a) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using coated mouse LIGHT (2 μg/ml) and supernatants of the hybridomas 9D10 and 15B2 (dilution 1 : 100). Sera of immunized mice at a dilution of 1 : 10 000 served as a positive control and conditioned RPMI medium as a negative control. For detection, an alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG) was used. (b) Dot blot analysis using supernatants of the hybridomas 9D10 and 15B2 and mouse LIGHT at the indicated concentrations including bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a negative control. Mouse LIGHT protein was detected using peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG as a secondary antibody. (c) ELISA using coated mouse LIGHT (2 μg/ml) and a dilution series of purified 9D10 and 15B2. Mouse IgG served as a negative control. For detection, an alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG was used.