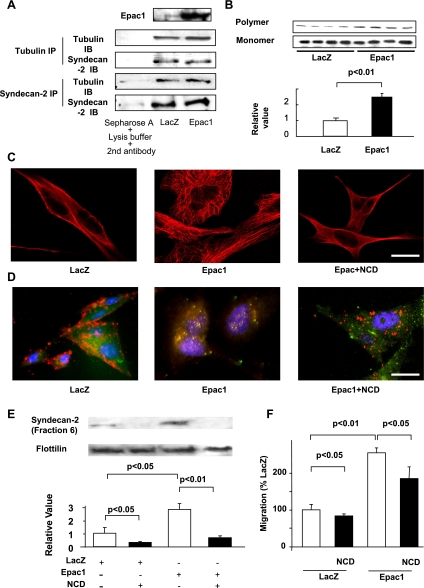
Fig. 3.
Epac increases syndecan-2 translocation by tubulin polymerization in SK-Mel-2. A: immunoprecipitation showed that syndecan-2 physically interacts with tubulin; however, Epac1 overexpression did not enhance the binding between syndecan-2 and tubulin. Epac1 was increased by Epac1 overexpression (top). B: immunoblots showed that Epac1 overexpression increases polymer form of tubulin. A bar graph shows the densitometric analysis of ratios of tubulin polymers to tubulin monomers. n = 4. C: immunocytochemistry for tubulin (red) is shown. Epac1 overexpression increased fine tubulin network, and such network formation was inhibited by nocodazol (NCD, 10 μM). Scale bar, 3 μm. D: immunocytochemistry for syndecan-2 (red) and lipid rafts (green) is shown. NCD (10 μM) decreased Epac1-induced syndecan-2 colocalization with lipid rafts (yellow). Scale bar, 3 μm. E: immunoblot showed that NCD (10 μM) decreased basal and Epac overexpression-induced syndecan-2 expression in lipid rafts-rich fraction. n = 4. F: migration assay showed that NCD (10 μM) decreased basal and Epac1 overexpression-induced cell migration. n = 4.