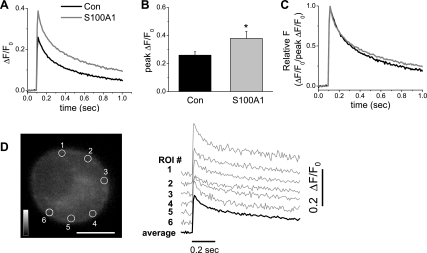
Fig. 12.
S100A1 amplifies Ca2+ transients evoked by single action potentials. Series of successive x-y confocal fluorescence images were recorded at high speed (108 fps) in cultured rat SCG neurons loaded with fluo-4 AM. A single Ca2+ transient was initiated by a 2-ms duration field stimulus applied 100 ms after the start of image acquisition. A: average time course of action potential-induced Ca2+ transients for control and S100A1-treated neurons. B: summary of effects of S100A1 on peak change in fluorescence over resting steady-state fluorescence (ΔF/F0) values. Extracellular addition of S100A1 to the medium induced a significant increase in the mean peak amplitude of the peripheral ΔF/F0 signals elicited by a single action potential (*P < 0.05; n = 14). C: action potential-evoked Ca2+ transients were normalized to peak ΔF/F0 values to compare the temporal properties of the Ca2+ transient shown in A. D: confocal x–y image of a fluo-4 AM-loaded SCG neuron; scale bar, 10 μm. ΔF/F0 time courses shown in A and B were calculated as the average (dark trace) of small circular areas selected at 6 positions within the neuron. The individual ΔF/F0 transients (gray traces) recorded from the 6 peripherally located ROI (circles) are displaced vertically for display.