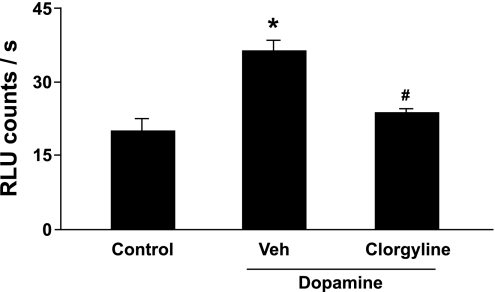
Fig. 7.
Dopamine-induced increase in superoxide in homogenates of human pulmonary valve (n = 3). Dopamine (1 mM) significantly increased superoxide levels in pulmonary valve compared with control tissue (incubated with PBS). The increase in superoxide produced by dopamine was attenuated by an MAO-A inhibitor (1 μM clorgyline). P < 0.05 vs. control (*) and vs. dopamine treatment (#).