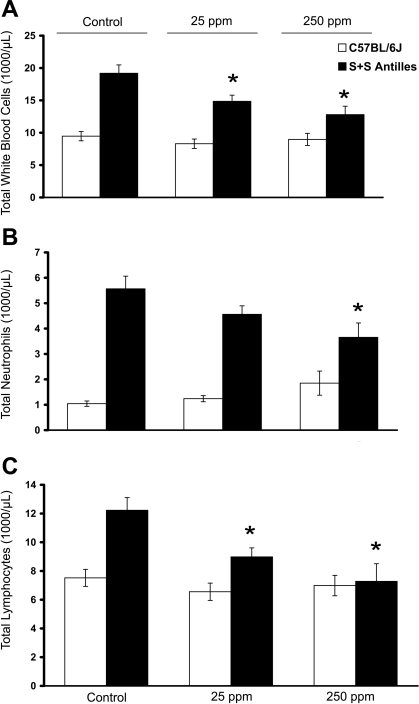
Fig. 1.
Inhaled carbon monoxide (CO) reduces white blood cell (WBC) counts in sickle cell disease mice. C57BL/6J (n = 10–12 mice/treatment group) and S+S-Antilles (n = 8 mice/treatment group) mice were treated with either 25 or 250 parts/million (ppm) inhaled CO for 1 h/day, 3 days/wk for 10 wk. Control animals were kept in ambient air. Blood was drawn at the end of 10 wk via cardiac puncture 24 h after the final CO treatment, and complete blood counts were measured. Total mean WBC (A), neutrophil (B), and lymphocyte (C) counts are shown by treatment group. Values are means ± SE. *P < 0.05 compared with untreated controls using ANOVA.