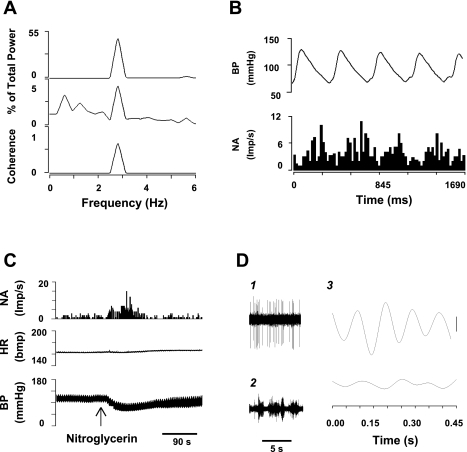
Fig. 5.
Characteristics of a cardiac sympathoexcitatory neuron in the rVLM. A: autospectra (AS) of arterial BP (top trace), rVLM neuronal activity (NA) (middle trace) and coherence (bottom trace). B: arterial pulse-triggered analysis of NA. Frequency domain analysis shows a significant coherence between BP and rVLM activity (0.69; A), while time domain analysis using pulse-triggered averaging demonstrated a relationship between BP and rVLM activity (B). C: changes in BP, heart rate (HR), and NA after intravenous administration of nitroglycerin (300 μg/kg). D: spike-triggered analysis of NA and inferior cardiac sympathetic nerve discharge (SND) suggests a relationship between NA and SND. 1, tracings of NA; 2, tracings of SND; 3, spike-triggered (top) and dummy-triggered (bottom) averages of SND. Vertical calibration is 10 counts.