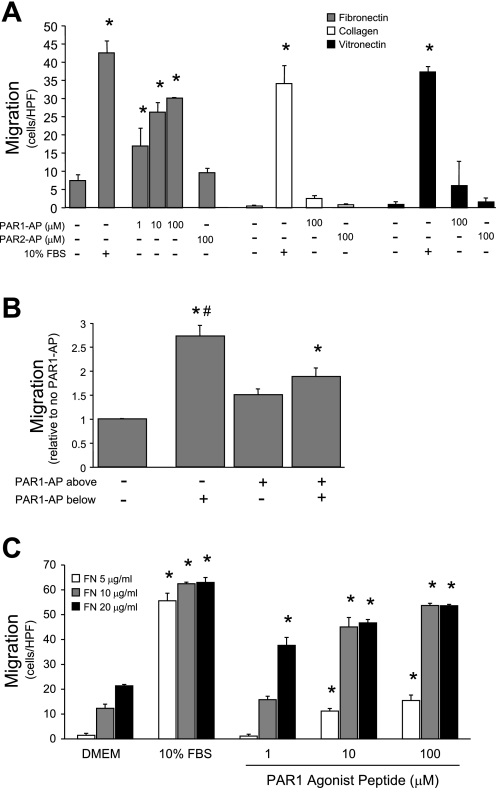
Fig. 2.
Protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1) activation induces FN-dependent rat pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell (RPMVEC) migration. Modified Boyden chamber filters were coated on both sides with the indicated extracellular matrix (ECM) protein. A: activation of the PAR1 receptor with PAR1 agonist peptide (SFLLRN, PAR1-AP) stimulated dose-dependent chemotaxis of RPMVEC when the cells were interacting with FN, but not with any other ECM protein tested. Migration in response to 10% FBS (positive control) did not differ significantly among the ECM proteins (*P < 0.05 vs. no agonist, n = 3). B: checkerboard assay performed by including PAR1-AP in the lower well (analogous to 2A), upper well (with cells), or both. PAR1-induced migration has both chemotactic and chemokinetic components (*P < 0.01 vs. no PAR1-AP; #P < 0.02 vs. PAR1-AP above and below, n = 3). C: modified Boyden assay with varying concentrations of FN coating. Increasing concentration of FN coating potentiated migration in response to low amounts of PAR1-AP (*P < 0.05 vs. DMEM, n = 3). HPF, high-powered field.