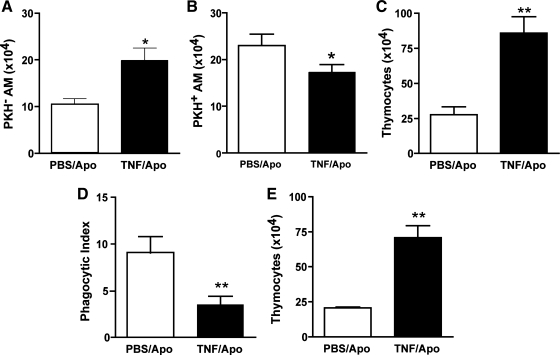
Fig. 2.
TNFα inhibits apoptotic cell clearance by alveolar macrophages in vivo at 90 min. PKH26-labeled apoptotic thymocytes (107 per mouse) were directly instilled into the tracheas of recipient mice simultaneously with TNFα (50 ng) or PBS as a control. Flow cytometry (A–C) and light microscopy (D and E) were used to assess efferocytosis. Macrophages were identified as F4/80+ events. The number of macrophages that were not associated with apoptotic cells (PKH− AM) was increased in TNFα-treated mice (A), whereas alveolar macrophages that were associated with apoptotic cells (PKH+ AM) were concomitantly decreased (B). This led to greater recovery of PKH-labeled thymocytes (C). The phagocytic index (number of apoptotic cells ingested per macrophage × 100) was reduced in mice treated with TNFα (D). Impaired removal of apoptotic cells from the lungs of TNFα-treated animals was further supported by an increased recovery of noningested apoptotic thymocytes (E). *P < 0.05 vs. control; **P < 0.01, n = 8 per group.