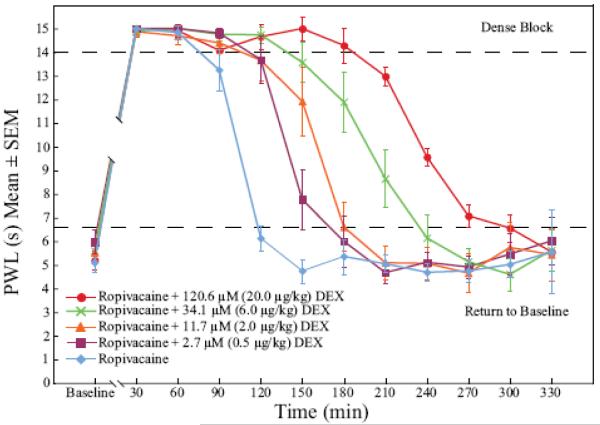
Figure 1.
Dexmedetomidine added to ropivacaine enhanced the duration of dense sensory blockade (p < 0.005) and time to return to normal sensory function (p < 0.005) in response to a thermal stimulus in a dose-dependent fashion when compared to the control group, ropivacaine alone. The graph shows the time-course of paw withdrawal latency values of the baseline taken 24 h before surgery (Baseline; mean value of all rats = 5.46 ± 1.13 seconds) and at 30-min time-points after the sciatic nerve block. DEX = dexmedetomidine; PWL = paw withdrawal latency.