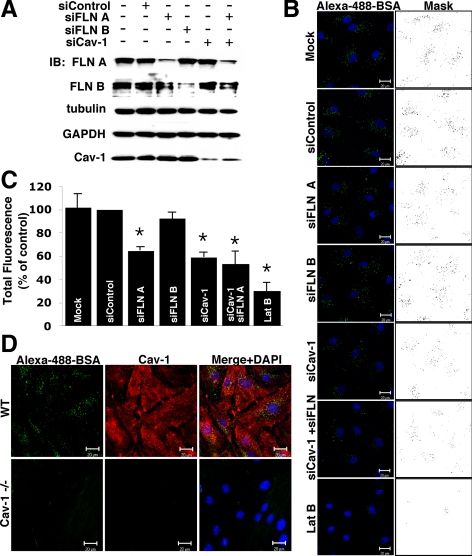
Figure 2.
Inhibition of caveolae-mediated endocytosis upon FLN A depletion. (A) HLMVECs were transfected with control, FLN A, FLN B, Cav-1, or a mixture of Cav-1 and FLN A siRNA, and the level of knockdown was examined 72 h after transfection. Western blot analysis confirmed that siRNA-mediated knockdown of FLN A, FLN B and Cav-1 was efficient and selective (see Supplemental Figure S1 for averaged data). (B) HLMVECs transfected with control, FLN A, FLN B, or Cav-1 siRNA alone, a mixture of FLN A and Cav-1 siRNA, or pretreatment with LatB (25 nM for 20 min) were incubated with Alexa-488-BSA (10 μg/ml) for 30 min and acid washed to remove cell surface-associated tracer albumin. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Images and masks of thresholded images are representative of three independent experiments. Bars, 20 μm. (C) Uptake of Alexa-488-BSA was quantified from thresholded images; the bar graph represents uptake as a percentage of BSA internalized by control siRNA-transfected cells (mean ± SEM; n = 3). Cells transfected with FLN A, Cav-1 and mixture of FLN A and Cav-1 siRNA showed 35%, 41 and 47% reduction in albumin uptake respectively in comparison with cells transfected with control siRNA (p < 0.05). Pretreatment with LatB reduced albumin internalization by 70%, whereas knockdown of FLN B did not induce statistically significant changes in BSA-uptake. (D) Endothelial cells purified from the lungs of wild type and Cav-1−/− mice were incubated with Alexa-488-BSA (10 μg/ml) for 30 min; acid washed; and then fixed, permeabilized, and stained for Cav-1. Cells from Cav-1−/− mice exhibited significantly reduced albumin uptake, suggesting caveolae-mediated uptake is the primary route of albumin internalization in endothelial cells.