Figure 4.
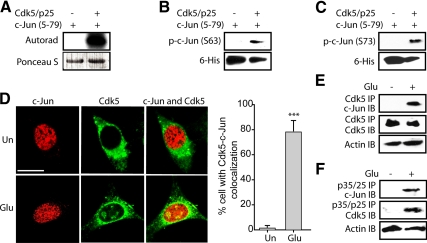
Cdk5 directly phosphorylates c-Jun at both Ser63 and Ser73 residues. (A) Recombinant c-Jun5–79 were phosphorylated by Cdk5–p25 complex using [γ-32P]ATP as described in Materials and Methods. The reaction mixture was incubated for 30 min at 30°C, after which proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membrane. The radioactivity associated with protein bands was visualized. (B and C) Recombinant c-Jun5–79 were phosphorylated by the Cdk5–p25 complex for 30 min at 30°C as described in Materials and Methods. The reaction mixture was then separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membrane, followed by probing using anti-phospho-c-Jun (Ser63) antibody and anti-phospho-c-Jun (Ser73) antibody, respectively. (D) Left, HT22 cells were treated with 5 mM glutamate for 45 min, followed by immunostaining with c-Jun (red) and Cdk5 (green) as described in Materials and Methods. Representative confocal images are shown. Un, untreated cells; Glu, glutamate. Scale bar, 20 μm. Right, the percentage of cells in which c-Jun and Cdk5 colocalized together was determined as described in Materials and Methods. The bar graphs show the mean; error bars, ±SEM (***p < 0.001). (E) HT22 cells were treated with 5 mM glutamate for 45 min, followed by immunoprecipitation using an antibody for Cdk5 as described in Materials and Methods. Immunocomplexes were then washed and subjected to Western blotting using c-Jun antibody. Ten percent of total cell lysates were used as control by probing with actin. (F) HT22 cells were treated with 5 mM glutamate for 45 min, followed by immunoprecipitation using antibody for p35/p25 as described in Materials and Methods. Immunocomplexes were then washed and subjected to Western blotting using c-Jun antibody. Ten percent of total cell lysates were used as control by probing with actin. All experiments were conducted at least three independent times, and representative results are shown.