Figure 8. PKA phosphorylates connexin 35 in Club endings.
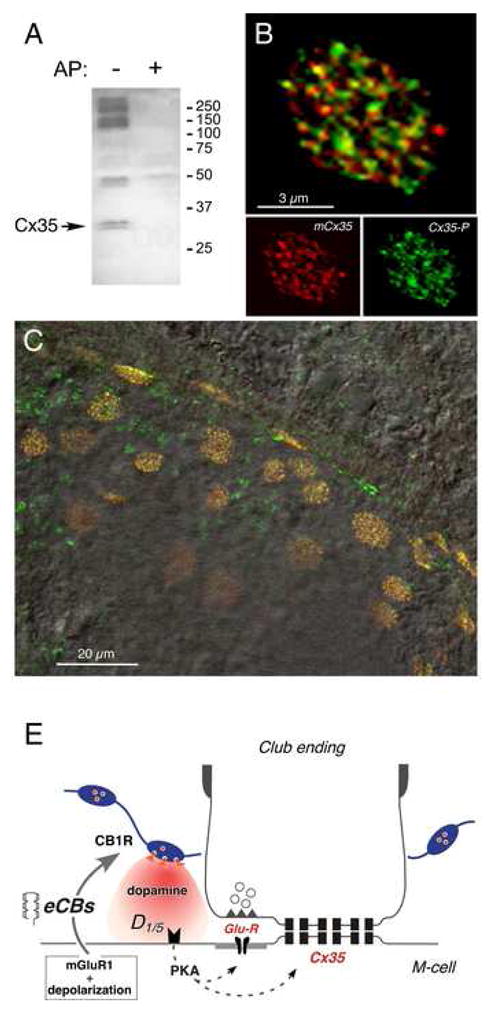
(A) Polyclonal anti-Cx35/P110 antibody recognizes Cx35 as a pair of bands at 32–33 kDa (arrow, left lane, AP-) in membranes from a small area of goldfish hindbrain where M-cells are located. Labeling is lost in membranes digested with alkaline phosphatase (right lane, AP+). The high molecular weight phospho-proteins labeled non-specifically by the antibody are not associated with Cx35 (Kothmann et al., 2007). 50 μg/lane crude membrane protein. (B) Laser scanning confocal immunofluorescence of a single Club ending with double-labeling by polyclonal anti-Cx35/P110 (green, Alexa fluor 488), and monoclonal anti-Cx35/36 (mCx35; red, Alexa fluor 594) antibodies. Top: superimposition of individual mCx35 and Cx35-P images (bottom), average of 3 confocal Z-sections (totaling 1.5 μm). (C) Lower magnification image showing extensive co-localization at individual Club endings in a section of the M-cell lateral dendrite. A DIC image of this region is superimposed. (D) Model for endocannabinoid-mediated potentiation of electrical and chemical synaptic transmission at Club endings. Synaptic activity leads to mGluR activation paired with postsynaptic membrane depolarization, triggering endocannabinoid (eCB) release from the postsynaptic M-cell dendrite, which activates CB1Rs on dopaminergic fibers. CB1R activation leads to dopamine release which, by activating postsynaptic D1/5 receptors, increases PKA activity responsible for simultaneous potentiation of electrical (Cx35) and glutamatergic (GluR) synaptic transmission.
