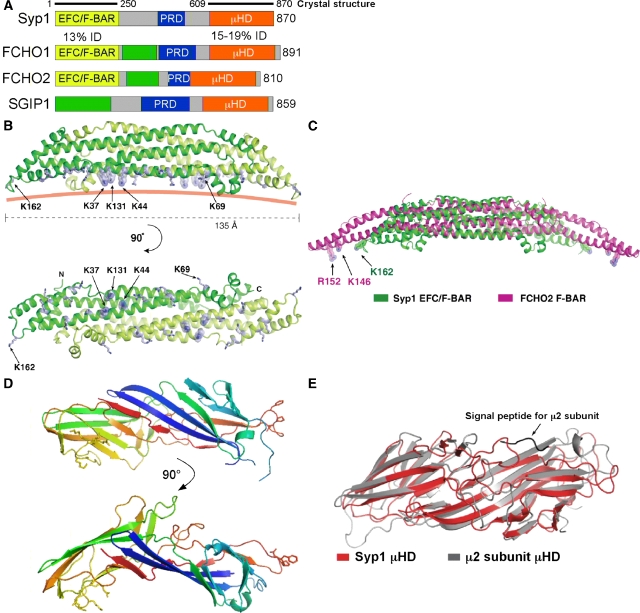
Figure 3.
Syp1 has EFC/F-BAR and μHD domains. (A) Human homologues of Syp1; % identity between the Syp1 domain and the human domains is indicated. EFC/F-BAR, extended FCH/FCH-BAR domain; PRD, proline-rich domain; μHD, μ-subunit homology domain; green box, region of homology shared by human proteins. (B) Structure of the Syp1 EFC/F-BAR domain dimer. The dimeric module is composed of two monomers (coloured in green and light green) related by two-fold crystallographic symmetry axis in the crystal. The basic Lys residues selected for mutagenesis on the membrane-binding surface are shown in stick models. The pink solid line shows a putative curvature of the membrane-binding surface of Syp1. (C) Alignment of the core helical bundles of the EFC/F-BAR domains of Syp1 (green) and FCHO2 (magenta). For the alignment of the central helix bundles, 75 Cα atoms from each monomer were used for superposition (see Materials and methods). (D) Structural model for the Syp1 μHD; the NPF (Asn-Pro-Phe) tripeptide motif is shown in stick models on the right side. (E) Superposition of the μHD domains of Syp1 (green) and μ2 subunit of AP-2 (magenta); 154 equivalent residues out of 262 residues in Syp1 μHD were selected for superposition, resulting in an r.m.s.d. of 1.58 Å.