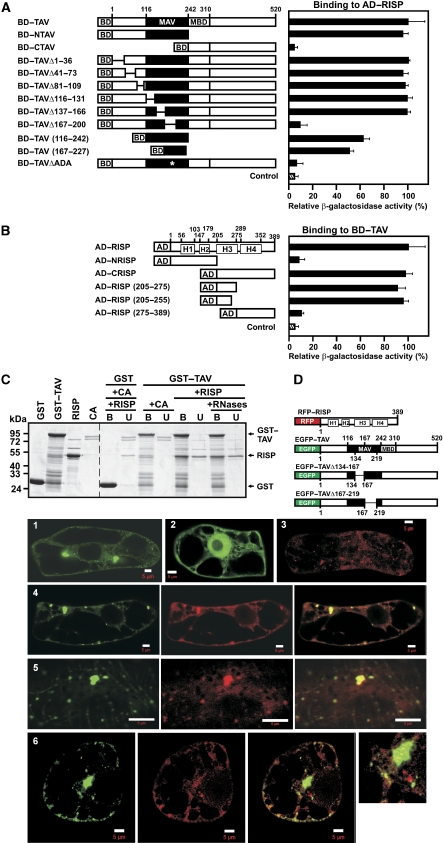
Figure 1.
Association of re-initiation supporting protein (RISP) with transactivator viroplasmin (TAV) and mapping of their interaction domains. (A) Interaction between TAV and its deletion mutants fused to the Gal4 binding domain (BD) and RISP fused to Gal4 activation domain (AD) in the yeast two-hybrid system was quantified by measuring β-galactosidase activity. The highest value of β-galactosidase activity in diploids transformed with both full-length constructs was taken as 100% (12 Miller units). MAV, minimal segment of TAV; and MBD, multiple protein-binding domain. (B) Quantification of interactions between RISP and its deletion mutants fused to Gal4 AD and BD-TAV. H1–H4 predicted coiled-coil domains. (C) GST and GST–TAV bound to glutathione beads were incubated with either purified recombinant RISP or Conalbumin (CA, 75 kDa). Lanes (+ RNases) show the experiment carried out in the presence of an RNase cocktail. The beads were washed, and the unbound (U) and bound (B) fractions were analyzed by SDS–PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. Right panel, Interactions of RISP with GST or GST–TAV; and left panel, purified GST, GST–TAV and RISP. (D) Schematic representation of full-length RISP fused to the C-terminus of RFP, and full-length TAV (or truncated versions) fused to the C-terminus of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP). Panels 1–6: Imaging fluorescence assays showing tobacco BY-2 cells transiently expressing EGFP–TAV (green, 1), EGFP alone (green, 2), or RFP-RISP (red, 3). 4 Left: EGFP–TAV, central: red fluorescent protein (RFP)–RISP, and right: merged. 5 Left: EGFP–TAVΔ134–167, central: RFP–RISP, right: merged. 6 Left: EGFP–TAVΔ167–219, central: RFP–RISP, right: merged; far right panel: high magnification image of part of the cell. Scale bars, 5 μm.