Figure 3.
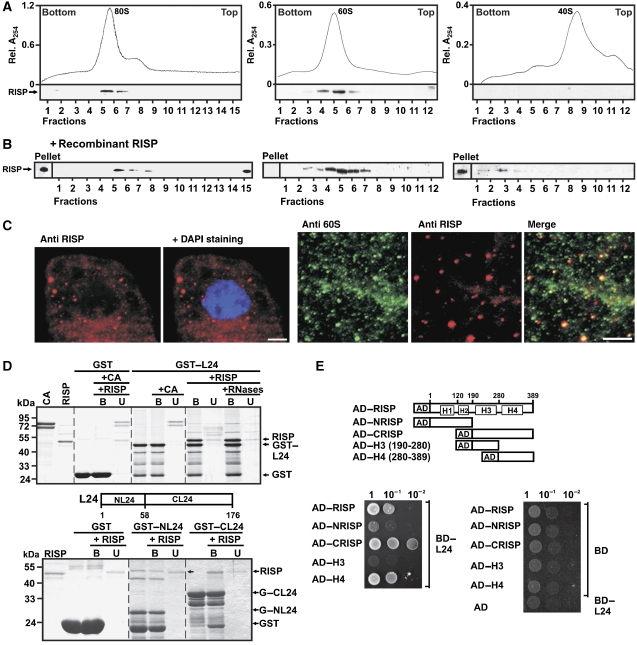
Re-initiation supporting protein (RISP) binds the 60S ribosomal protein L24 and co-sediments with 60S and 80S. (A) RISP co-sediments with 80S (left), and 60S (middle) but not with 40S (right) ribosomes. Lower panels: immunostaining of gradient fractions with antibodies against RISP. (B) 80S, 60S and 40S were incubated with recombinant RISP at approximately 1:1 molar ratio before being subjected to sucrose density gradient centrifugation as in (A) followed by western blot analysis with antibodies against RISP. (C) Left panels: Immunofluorescence assays showing localization of RISP (red) within cytoplasm of BY-2 cells. Nucleus was stained with DAPI (blue); right panels: colocalization of endogenous 60S (green) and RISP (red) in BY-2 tobacco cells; only part of the cytoplasmic compartment is shown. Anti-60S and anti-RISP images were merged in the right-most panel. Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) RISP interacts with the C-terminal region of L24 in GST pull-down assay. RISP or the control protein CA was incubated with recombinant L24 fused to GST (GST–L24, upper panel). Lanes labelled +RNases show the experiment carried out in the presence of an RNase cocktail. RISP was mixed with either the N- or C-terminus of L24 fused to GST (GST–NL24 and GST–CL24; bottom panel) bound to glutathione beads. The beads were washed, and purified bound (B) and unbound (U) proteins were resolved by SDS–PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. (E) Yeast two-hybrid interactions between BD–L24 and RISP and its deletion mutants fused to AD. Equal OD600 units and 1:1, 1:10 and 1:100 dilutions were spotted from left to right and incubated for 2 days.