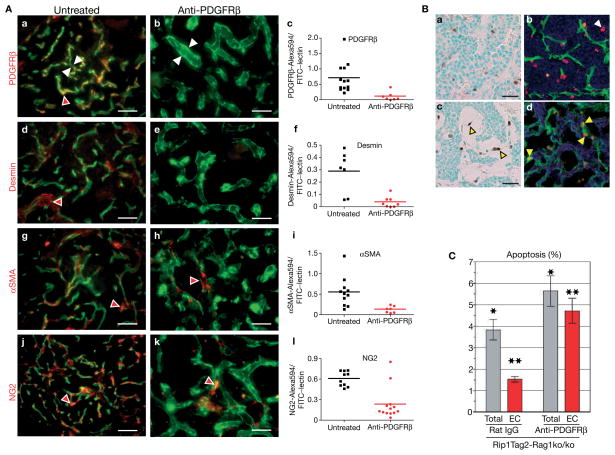
Figure 5.
Inhibition of PDGFRβ signalling depletes pericytes and increases endothelial cell apoptosis. (A) Anti-PDGFRβ treatment in immunocompromised Rip1Tag2-Rag1ko/ko mice depletes tumour pericytes. Ten-week-old Rip1Tag2-Rag1ko/ko mice (n = 8) were subjected to rat anti-mouse PDGFRβ or saline (control) for 3 weeks. Mice were injected intravenously with FITC-labelled tomato lectin prior to sacrifice to visualize the vasculature in green. Subsequently, tumour sections of control and treated mice were stained with a red-labelled antibody for PDGFRβ (a, b), desmin (d, e), αSMA (g, h) or NG2 (j, k). In contrast to control tumours, very few pericytes were observed in treated tumours (red arrowheads). Pericyte-depleted blood vessels were enlarged and hyperdilated with vessels in control tumours (white arrowheads). Quantitative evaluation of the number of PDGFRβ+ (c), desmin+ (f), αSMA+ (i) and NG2+ (l) cells was revealed on control and treated tumour sections by red antibody staining. The total area of red staining within the tumour boundaries within each image (7–13 images per set) was quantified using Improvision’s Volocity 2.6.1. Statistical analysis was performed with an unpaired t-test comparing the pericyte coverage of control-treated to anti-PDGFRβ tumours. P values were considered statistically strongly significant (P < 0.01).
(B) Anti-PDGFRβ treatment in Rip1Tag2-Rag1ko/ko mice increases endothelial cell apoptosis in tumours. Apoptotic cells in tumours of control (a, b) and anti-PDGFRβ-treated mice (c, d) were detected by TUNEL staining. Whereas apoptotic cells are more randomly distributed in control tumours (a), they are predominantly apparent in hyperdilated blood vessels of anti-PDGFRβ-treated tumours, reflecting endothelial cells undergoing apoptosis (c; yellow arrowheads). Co-staining of TUNEL-positive cells with an antibody against CD31 revealed the apoptotic index of endothelial cells in tumours of control rat IgG (b; white arrowhead) and anti-PDGFRβ-treated Rip1Tag2 mice (d; yellow arrowheads). (C) The apoptotic index of all cells (total) and endothelial cells (EC) in tumours of control rat IgG and anti-PDGFRβ-treated Rip1Tag2 mice. Six to seven tumour images containing a total of over 7,000 cells per group were used to determine the apoptotic index of the total cell population and the endothelial cell population within tumours. Statistical analysis comparing the rat IgG control group to the anti-PDGFRβ-treated group was performed with a two-tailed, unpaired t-test and P values were considered statistically significant (*P = 0.0038 for total apoptosis; **P = 0.0059 for endothelial cell apoptosis). Scale bars, 9.7 mm (A), 9.9 mm (B, a, c).