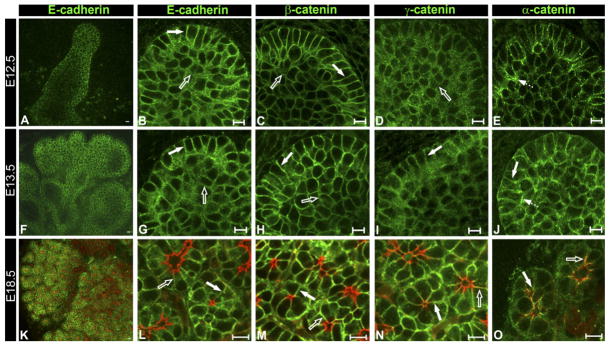
Fig. 4.
Organization of E-cadherin junctions during SMG morphogenesis. SMG buds were immunostained with antibodies to E-cadherin (A,B, F,G, K,L), β-catenin (C,H,M), γ-catenin (D,I,N), and α-catenin (E,J,O) and examined by confocal microscopy. Low-power confocal imaging of E-cadherin in E12.5 (A), E13.5 (F), and E18.5 (K) SMGs. High-resolution confocal imaging through the center of the E12.5 buds revealed that E-cadherin and β-catenin were tightly focused at the lateral surfaces of cells at the bud’s periphery (B,C, block arrows), while cells in the interior exhibited diffuse staining (B,C, open arrows). γ-catenin staining was diffuse in both the peripheral cells and the cells in the bud’s interior (D, open arrow). α-catenin was more intense in the apical domains of the peripheral cells (E, broken arrow). Scale bar = 10 μm. Confocal imaging through the center of E13.5 buds revealed cells with columnar morphology in the outer layer (G–J, block arrows), with E-cadherin and β-catenin tightly focused at the lateral interfaces (G and H, block arrows). The interior regions exhibited more diffuse staining for E-cadherin and β-catenin (G and H, open arrows) than in the peripheral cells. γ-catenin was localized at the lateral borders in the peripheral layer (I, block arrow). α-catenin was detected at the lateral surfaces of cells in the peripheral layer and, prominently, at their apical membranes (J, broken arrow). Scale bar = 10 μm. L–O: E18.5 SMGs were immunostained for E-cadherin, β-catenin, γ-catenin, and α-catenin, counterstained for F-actin with rhodamine-phalloidin (red), and examined by confocal microscopy. Within the acini (block arrows) and ducts (open arrows), E-cadherin, β-catenin, and γ-catenin localized to cell–cell interfaces (L–N, respectively), while α-catenin displayed prominent colocalization with F-actin at the apical domains (O). Scale bar = 10 μm.