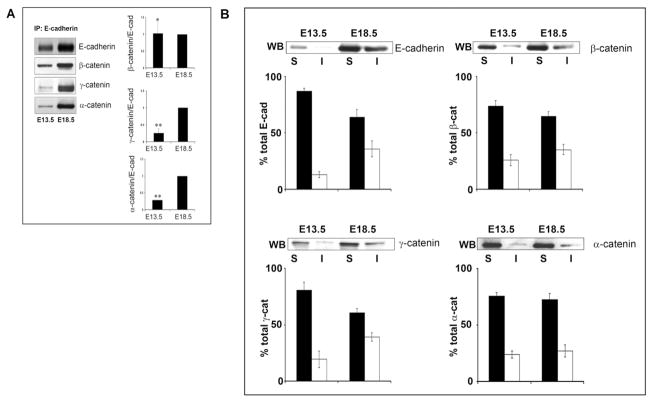
Fig. 6.
SMG development is accompanied by changes in the molecular composition and Triton solubility of E-cadherin junctions. A: Total tissue extracts from E13.5 and E18.5 SMGs were immunoprecipitated (IP) with the antibody to E-cadherin and analyzed for association of β-, γ-, and α-catenins by Western blot. While there was little change in β-catenin’s association with E-cadherin as the SMG developed, both γ- and α-catenin showed increased interaction from E13.5 to E18.5. Bar graphs reflect E13.5 values normalized to E18.5 for determining the ratio of each catenin in the E-cadherin complex and represent an average of three experiments. Data were normalized to E18.5 values and plotted ± SEM. (*, no significant difference; **P < 0.05). B: Diminished Triton solubility of E-cadherin and catenins was associated with SMG development. SMGs were extracted with the Triton buffer and Triton-soluble (S) and -insoluble (I) fractions were analyzed by Western blot with antibodies to E-cadherin, β-catenin, γ-catenin, and α-catenin. Bar graphs depicting quantification of the immunoblots are shown (filled bars, Triton-soluble; unfilled bars, Triton-insoluble). E-cadherin, β-catenin, and γ-catenin displayed increased association with the Triton-insoluble fraction in E18.5 SMG compared to early morphogenesis. Little change was observed for α-catenin. Bar graphs represent an average of three independent experiments, except for the γ-catenin data, which was based on two separate studies. Values are plotted as ± SEM.