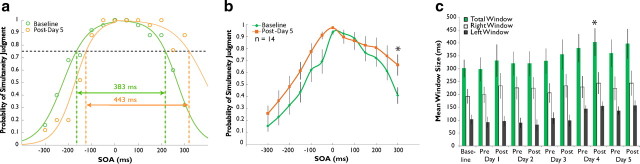
Figure 3.
Changes in the multisensory temporal binding window are not seen following passive exposure. a, As in the training participants, individual single-assessment data were fit with two sigmoid curves to derive an estimation of the temporal binding window in exposure controls. b, Control participants (n = 14) exposed to the same stimulus pairs as training participants showed a significant increase in probability of simultaneity judgment after exposure. c, This was manifested as a significant increase in window size over the course of a week of exposure. Error bars indicate 1 SEM, *p < 0.05.