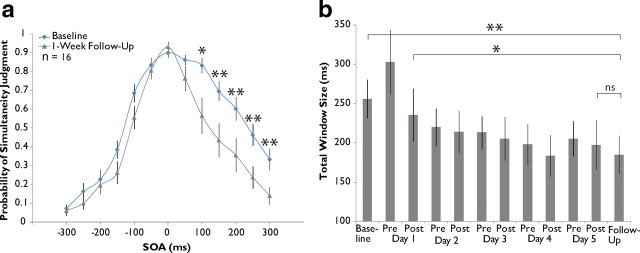
Figure 4.
Training-induced changes in the multisensory temporal window are stable over time. a, Grand averaged data from 14 of the original 22 training subjects during 1 week follow-up assessment compared with baseline. Significant decreases in probability of simultaneity judgment are seen exclusively on the right side of the distribution. b, Assessment across the 14 subjects shows a stable narrowing of window size from baseline. Error bars indicate 1 SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.