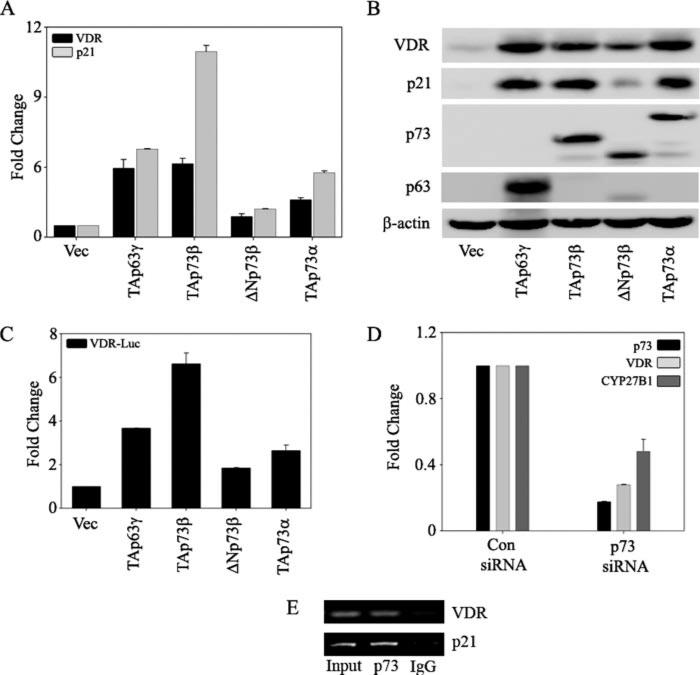
FIGURE 4. p73 is essential for endogenous VDR expression.
H1299 cells were transfected with control vector, TAp63γ, TAp73β, ΔNp73β, or TAp73α as indicated. A, at 24 h post-transfection, total RNA was extracted to perform TaqMan reverse transcription-PCR to quantitate the transcript levels of VDR and p21 as indicated. The y axis represents the -fold change in mRNA levels of VDR and p21 compared with empty vector-transfected cells. B, at 24 h post-transfection, total protein was extracted to detect the endogenous VDR and p21 protein levels by using anti-VDR and anti-p21 antibodies, respectively. Ectopic expression of TAp63γ, TAp73β, ΔNp73β, and TAp73α was confirmed by using antibodies specific for p63 and p73. C, H1299 cells were co-transfected with full-length VDR promoter reporter along with the indicated plasmids. At 24 h post-transfection, cells were harvested in PLB and subjected to dual luciferase assays. RLU/R-Luc ratios were calculated to normalize for transfection efficiency. The y axis represents -fold change relative to empty vector control. D, H1299 cells were transfected with either control (Con) siRNA or p73 siRNA by using the calcium phosphate method as described under “Experimental Procedures.” At 48 h post-transfection, RNA was extracted and subjected to TaqMan real time PCR to detect p73, VDR, and CYP27B1. E, chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis was performed on H1299 cells as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Formaldehyde-cross-linked chromatin was immunoprecipitated with anti-p73 or normal IgG antibodies as indicated. Eluted DNA was PCR-amplified with primers specific for VDR and p21. p21 promoter amplification was used as a positive control for p73.