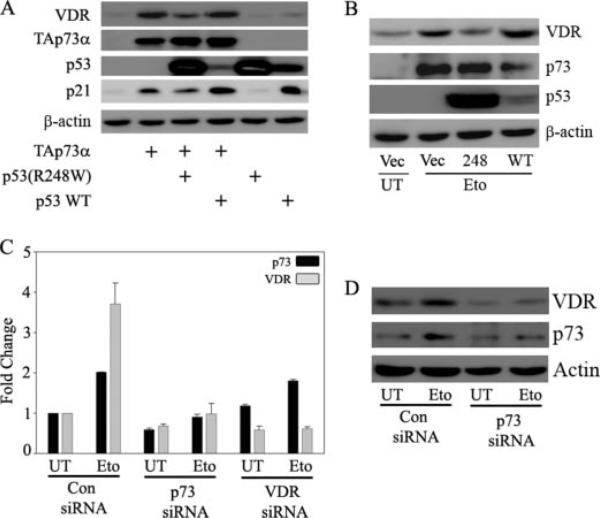
FIGURE 5. p73 is required for DNA damage-induced expression of VDR.
A, H1299 cells were transfected with control vector or expression plasmids encoding TAp73α, p53 wild type (WT), and p53 (R248W) mutant alone or in combination as indicated. At 24 h post-transfection, total protein was extracted for immunoblot analysis to detect the endogenous VDR protein levels. B, H1299 cells were transfected with empty vector or p53 (R248W) or p53 wild type as indicated. The next day, cells were either untreated (UT) or treated with 8 μm etoposide (Eto) as indicated. Whole cell lysate was prepared and endogenous VDR, and p73 protein levels were detected using anti-VDR and anti-p73 antibodies, respectively. Overexpression of wild type p53 and mutant p53 (R248W) was confirmed by using p53-specific antibody, and detection of β-actin was used to confirm equal amounts of protein loading. C and D, H1299 cells were transfected with control siRNA, VDR siRNA, or p73 siRNA as described under “Experimental Procedures,” and 24 h post-transfection, cells were trypsinized and replated onto 6-well plates. After cells adhered properly in wells, cells were treated with 8 μm etoposide or left untreated as indicated. At 12 h post-treatment, cells were harvested for either RNA or whole cell extract. TaqMan real time PCR was performed to detect the mRNA levels of p73 and VDR. Immunoblot analysis was performed to detect the endogenous VDR and p73 protein levels using anti-VDR and anti-p73 antibodies, respectively.