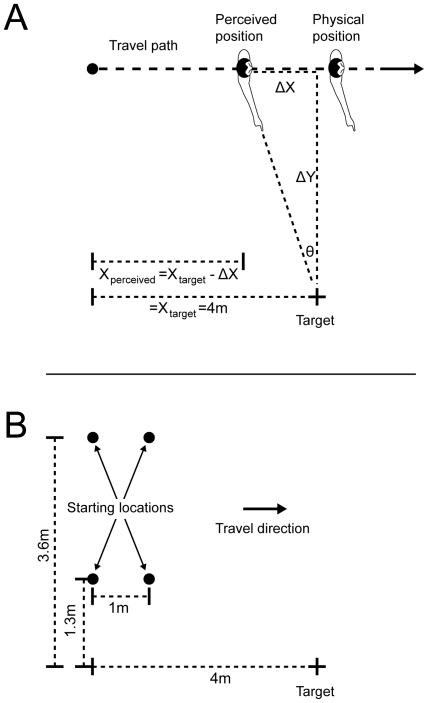
Figure 1. General procedure.
A) Participants began each trial at one of several target-relative starting locations. After viewing the target, they moved or imagined moving past it along a straight travel path. While they moved, they pointed continuously to the spatial image of the target (or to the actual target during sighted walking). For the actual self-motion trials (SW and BW), based on arm angle and the known value of y, we computed x, or perceived distance from the target, throughout each movement trial. As shown here, there may be a discrepancy between a participant's perceived and actual location which would indicate a misperception of self-motion. The extent of arm movements used for analyses was within a comfortable and unconstrained motion range. B) Four different target-relative starting locations were used for this task.