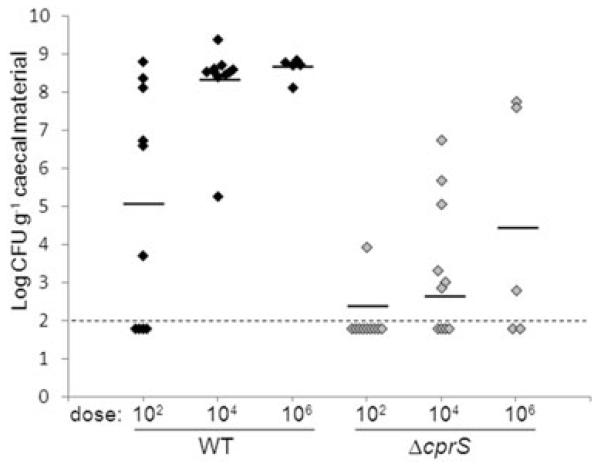
Fig. 6.
ΔcprS displays a dose-dependent chick colonization defect. One-day-old chicks were orally challenged with the indicated number of cfu of WT (black diamonds) or ΔcprS (grey diamonds) bacteria. Six days post infection, birds were sacrificed, and caecal colonization levels were determined by plating on C. jejuni-selective MH agar. Each data point represents the log cfu g−1 recovered from an individual chick, with the average recovery for each dosage denoted by a black bar. The limit of detection (100 cfu) is denoted by the thin dashed line.