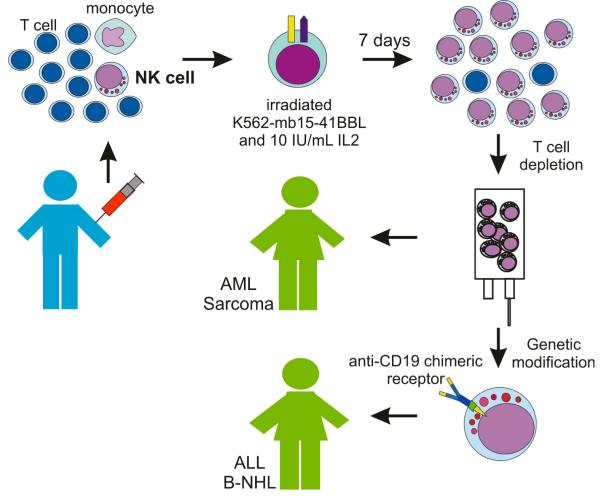
Figure. Schematic representation of protocols using expanded NK cells at St Jude Children’s Research Hospital.
The leukapheresis product obtained from a haploidentical donor is mixed with irradiated K562-mb15-41BBL cells. After 7 days of culture, most cells recovered are activated NK cells. After T-cell depletion using the CliniMACS system, NK cells are infused in patients with NK-sensitive malignancies such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML), Ewing sarcoma or rhabdomyosarcoma. For patients whose neoplasia is less sensitive to NK cytotoxicity, such as B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) or B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL), expanded NK cells are transduced with an anti-CD19 chimeric receptor before infusion.