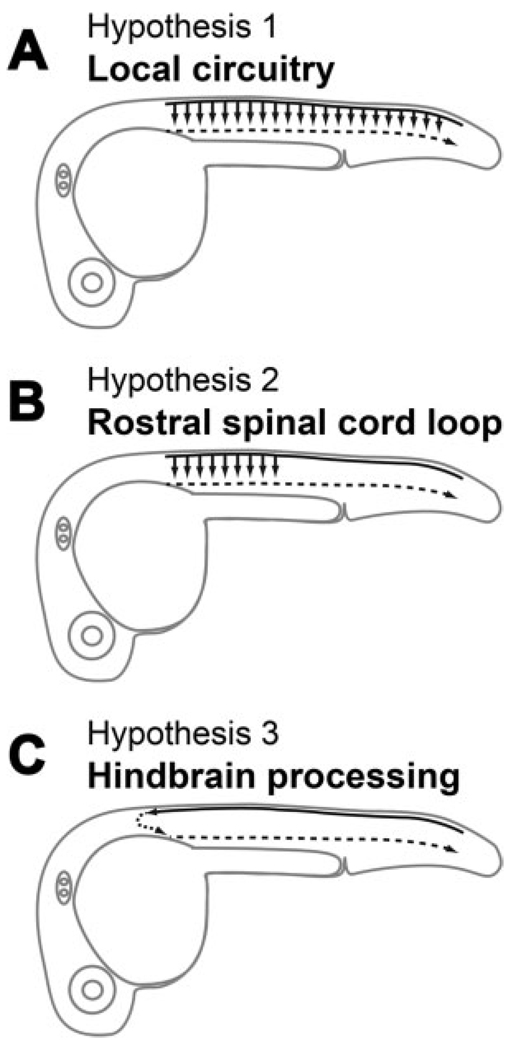
Figure 1.
Diagram of the potential circuitry underlying the touch response. (A) Sensory input may be relayed locally all along the spinal cord for transmission to motoneurons. (B) Sensory input is routed through spinal interneurons in rostral spinal cord before reaching the motoneurons. (C) Sensory input is processed in the hindbrain that then drives the motoneurons.