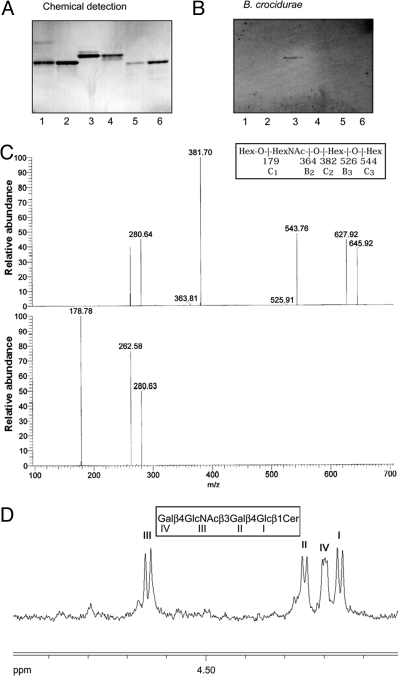
Fig. 5.
Isolation and characterization of a Borrelia-binding GSL from human erythrocytes. Binding of Borrelia to GSLs on thin-layer chromatograms. Chemical detection by anisaldehyde (A), and autoradiogram after adherence of 35S-labeled B. crocidurae CR2A (B). Lane 1, H type 2 pentaglycosylceramide (Fucα2Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer) from human erythrocytes, 4 μg; lane 2, B5 pentaglycosylceramide (Galα3Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer) from rabbit erythrocytes, 4 μg; lane 3, Borrelia-binding GSL isolated from human erythrocytes, 4 μg; lane 4, Forssman pentaglycosylceramide (GalNAcα3GalNAcβ3Galα4Galβ4 Glcβ1 Cer) from canine intestine, 4 μg; lane 5, iso-Forssman pentaglycosylceramide (GalNAcα3GalNAcβ3Galα3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer) from rat colon carcinoma, 2 μg; lane 6, para-Forssman pentaglycosylceramide (GalNAcβ3GalNAcβ3 Galα4 Galβ4Glcβ1Cer) from human erythrocytes, 4 μg. Autoradiography was performed for 48 h. (C) MS2 spectrum of the [M-H]− ion of m/z 706 of the saccharide derived from the Borrelia-binding GSL isolated from human erythrocytes (retention time 29 min) (upper chart) and MS3 spectrum of the [M-H]− ion at m/z 382 (lower chart). (D) Anomeric region of the 500 MHz proton NMR spectrum of the Borrelia-binding GSL fraction isolated from human erythrocytes (30 °C).