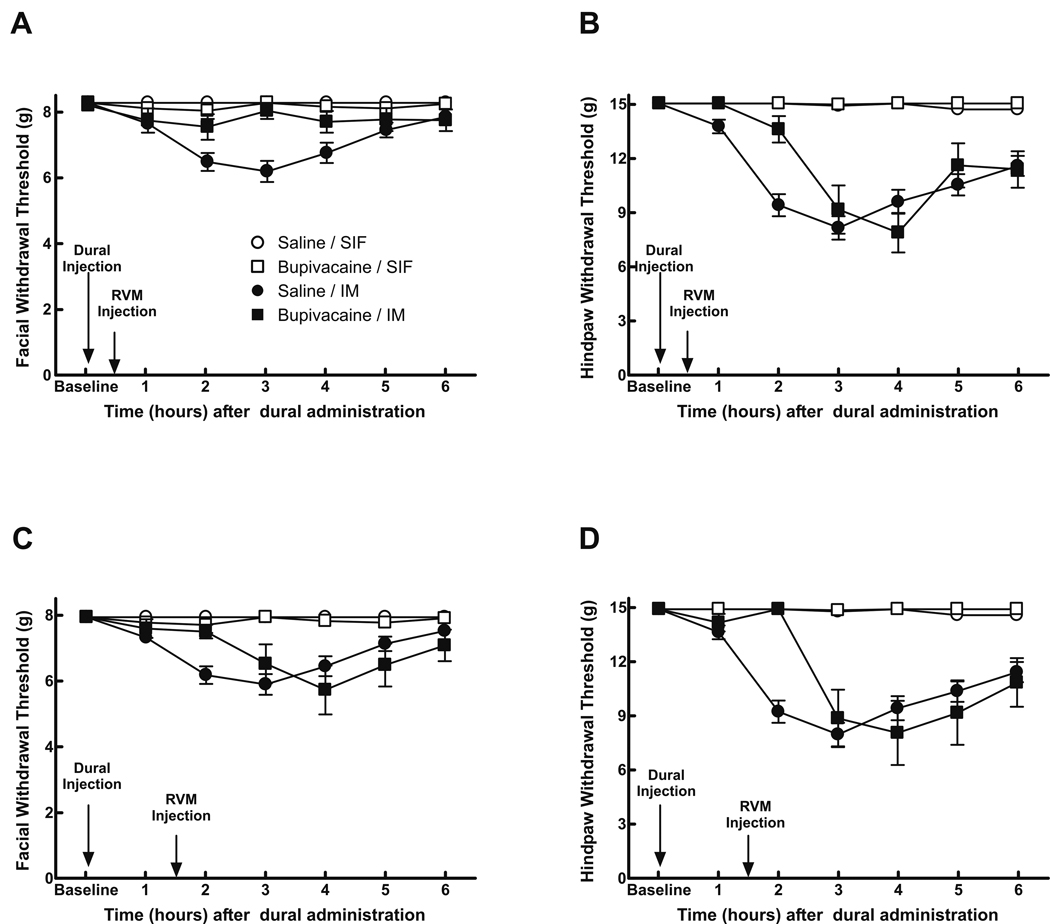
Fig 5.
Rats received dural administration of IM or SIF and also received bupivacaine (0.5% w/v) microinjected into the RVM either 0.5 or 1.5 hr afterwards. Bupivacaine given 0.5 hr after IM blocked the appearance of behavioral signs of facial allodynia (A) and attenuated the development of hindpaw allodynia in a time-dependent, reversible manner (P = 0.0007) (B). When bupivacaine was given 1.5 hr following dural administration of IM, it also significantly (P < 0.05) and reversibly attenuated behavioral signs of allodynia in both the facial region (C) and the hindpaws (D). Behavioral responses were not altered by bupivacaine in SIF rats or saline in SIF rats (data not shown).