Figure 4.
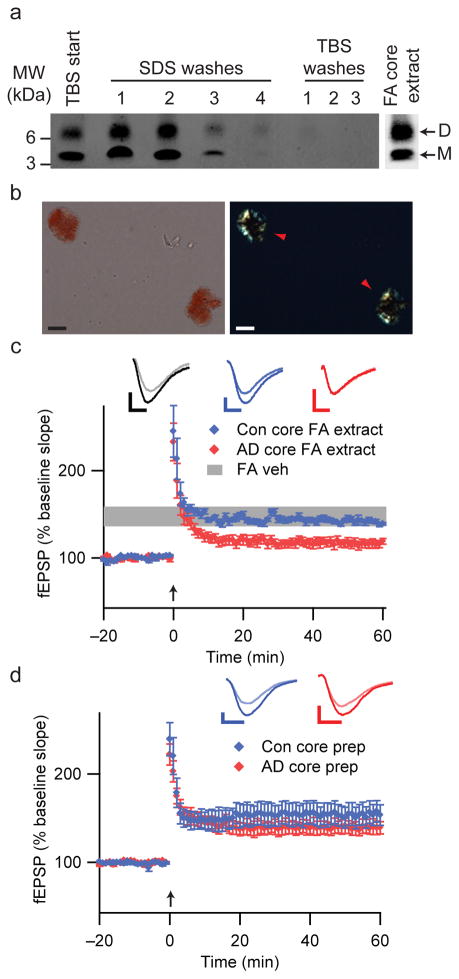
Insoluble amyloid cores contain Aβ dimers with synaptotoxic potential but are not readily released. (a) IP/WB of sequential extracts of the TBS-insoluble pellet prepared from 100 mg of a plaque-rich AD brain (case AD 5 from Fig. 2a) (see Methods). The final TBS washes reveal that no additional soluble Aβ can be extracted from the pellet after 4 sequential SDS washes. The remaining core-rich pellet was then incubated in formic acid (FA core extract) and analyzed by IP/WB, revealing that the insoluble cores contain Aβ monomers and dimers (far right lane). (b) Core preps following the final TBS wash as in Fig. 4a were stained with 0.2% Congo red and visualized by brightfield (left) and polarization (right) microscopy. Isolated amyloid cores display characteristic birefringence with Congo red (red arrowheads). Material prepared similarly from Con 3 (Fig. 2a) did not contain any such structures. Scale bar = 5 μm. (c) Cores prepared as in Figs. 4a, b were extracted with 88% formic acid and neutralized with NaOH. Summary LTP data for slices treated with just FA/NaOH vehicle (FA Veh, n=5), or with FA/NaOH core extracts from AD (AD core FA extract, n=7) or control (Con core FA extract, n=5) brains. Calibration bars, 5 msec/0.2 mV. (d) Summary LTP data for slices exposed to intact core preps isolated as in Fig. 4a, b from 100 mg AD cortex (AD core prep, n=5) or Con cortex (Con core prep, n=5). Calibration bars, 5 msec/0.3 mV.