FIG. 1.
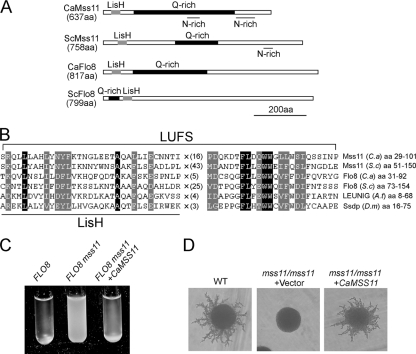
C. albicans Mss11 is a functional homolog of S. cerevisiae Mss11. (A) Schematic depiction of the LisH domain (gray box), glutamine-rich (Q-rich) regions (black box), and asparagine-rich (N-rich) regions (underlined areas) in the CaMss11, ScMss11, CaFlo8, and ScFlo8. aa, amino acids. (B) Sequence alignment of the LUFS domain between CaMss11 and other regulatory proteins. Identical residues are shaded in black and conserved residues are shaded in gray. The multiplication sign (×) and subscript numbers indicate spacing between the motifs in the LUFS domain. (C) Ectopically expressed CaMSS11 suppresses the nonflocculent phenotype of a haploid mss11 mutant. S. cerevisiae strains CZS1 (FLO8) carrying pVT102U and CZS2 (FLO8 mss11) carrying pVT102U or pVT102U-CaMSS11 were grown in SCD to saturation, allowed to settle for 5 min, and then photographed. (D) Ectopically expressed CaMSS11 suppresses the pseudohyphal growth defect of a diploid mss11 mutant. S. cerevisiae strains MLY61 (WT) carrying pVT102U and MLY181a/α (mss11/mss11) carrying pVT102U or pVT102U-CaMSS11 were grown on SLAD plates at 30°C for 5 days.