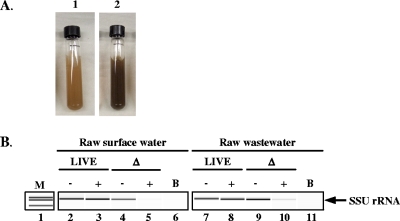
FIG. 5.
Detection of C. parvum oocysts in Ohio River and raw wastewater samples, using CryptoPMA-PCR. (A) Environmental samples spiked with oocysts prior to immunomagnetic separation, PMA treatment, and PCR. Resuspended 0.4-ml pellet from raw surface water concentrate (panel 1) and raw wastewater (panel 2). (B) SSU rRNA gene PCR amplicons from live and dead oocysts spiked in raw surface water or raw wastewater. Amplification of a portion of the SSU rRNA gene was performed using PCR (lanes 2 to 11). Gel electrophoresis analysis was performed using an Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100. M, marker; −, no PMA; +, PMA added; Δ, oocysts treated at 70°C; B, blank sample that did not receive oocyst spike. Data represent the results of one of two independent experiments performed.