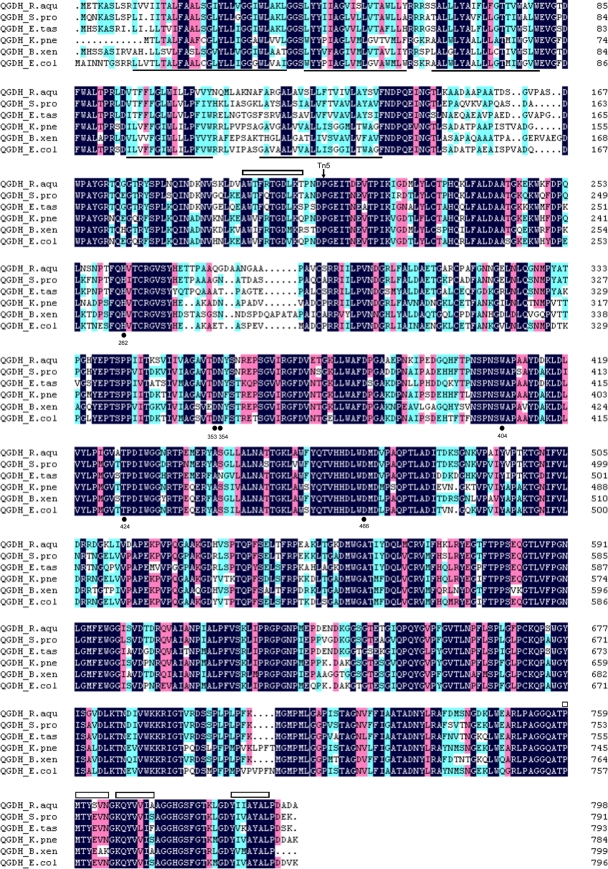
FIG. 5.
Alignment of deduced gdh amino acid sequence with sequences of diverse members of the GDH family. Proteins whose sequences have similarities with the amino acid sequence deduced from gdh include QGDH_S.pro (81.5%) from Serratia proteamaculans 568 (GenBank accession number ABV42200), QGDH_E.tas (75.7%) from Erwinia tasmaniensis Et1/99 (accession number YP_001908309), QGDH_K.pne (71.6%) from Klebsiella pneumoniae 342 (accession number YP_002240396), QGDH_B.xen (71.2%) from Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 (accession number YP_555448), and QGDH_E.col (70.3%) from Escherichia coli (accession number P15877). Regions of transmembrane helices determined for GDH (55) and predicted for QGDH-HX2 are underlined. Functionally important residues located in the active sites binding to Ca2+ and PQQ are numbered and denoted with “•,” and the predicted so-called “propeller fold” region is indicated by “□.” The solid arrow indicates the Tn5 insertion site.