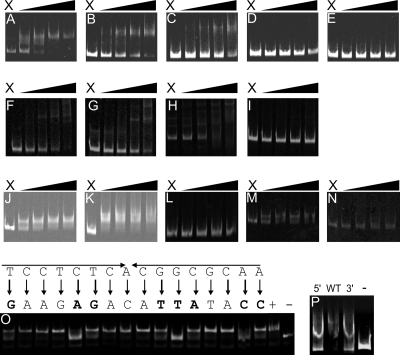
FIG. 2.
(A to E) EMSAs of H6-HspR interaction with DNA fragments encompassing the promoter regions of dnaK (A), clpB (B), clgR (C), nfo (D), and hrdB (E). DNA fragments were obtained by PCR using IRD-800-labeled primers. Lane X contained the probe without added protein. The remaining lanes contained probe samples incubated with increasing concentrations of H6-HspR (concentrations ranged from 50 to 400 nM). For each successive lane from left to right, the concentration of H6-HspR was doubled. (F to I) EMSAs of H6-HrcA interactions with promoter regions of hrcA (F), groEL (G), groES (H), and hspR (I) (negative control). DNA fragments were obtained by PCR using IRD-800-labeled primers. Lane X contained the probe without added protein. The remaining lanes contained probe samples incubated with increasing concentrations of H6-HrcA (concentrations ranged from 50 to 400 nM). For each successive lane from left to right, the concentration of H6-HrcA was doubled. (J to N) EMSAs of H6-ClgR-T interactions with promoter regions of clpC (J), clpP (K), clgR (L), and hrcA (M). Panel N represents an EMSA in which full-length ClgR was used in combination with the labeled promoter region of clpC. DNA fragments were obtained by PCR using IRD-800-labeled primers. Lane X contained the probe without added protein. The remaining lanes contained probe samples incubated with increasing concentrations of H6-ClgR-T or H6-ClgR (concentrations ranged from 15 to 120 nM). For each successive lane from left to right, the concentration of H6-ClgR-T or H6-ClgR was doubled. (O) EMSAs of H6-ClgR-T with a concentration of 60 nM on mutated promoter regions of the ClgR motif of PclpC. Original sequences and mutations are shown above the image. +, original promoter sequence; −, promoter region of hsp20. (P) EMSAs of H6-HspR with a concentration of 175 nM on mutated promoter regions of the HAIR motif of PclpB. N, mutation of the AAAA 3′ extension to GGGG; WT, original promoter sequence; and C, mutation of the TTTT 5′ extension to CCCC.